How a septic tank works using separation
Here is an easy-to-understand description of how a septic tank works using separation.
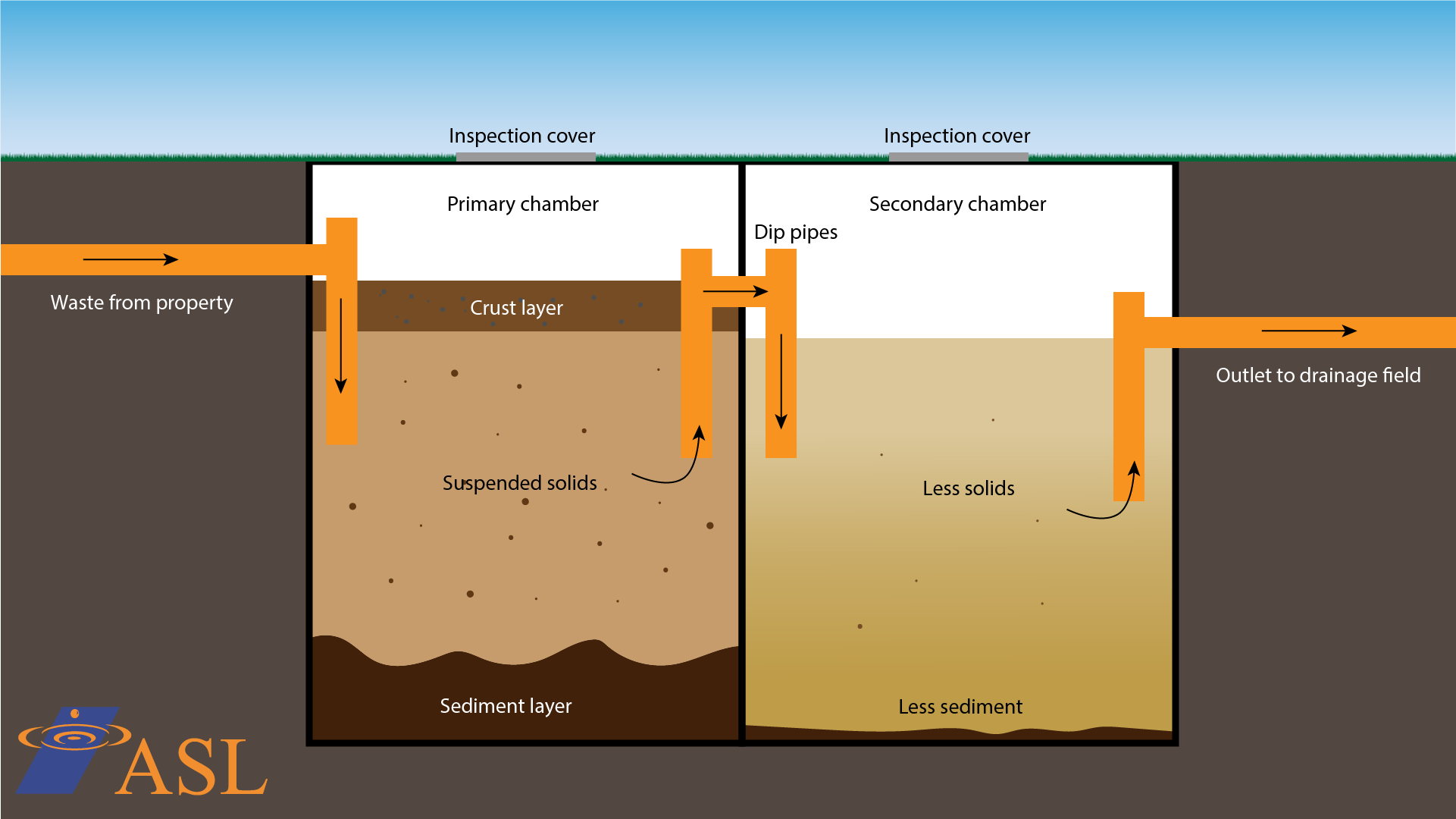
A septic tank is a key component of a wastewater treatment system commonly used in homes and buildings not connected to a municipal sewage system. It works through a process of separation and natural biological decomposition. Here's how it works:
-
Wastewater collection: When you use water in your home for activities like flushing toilets, taking showers, and washing dishes, the wastewater from these activities flows into the septic tank through a network of pipes. This wastewater includes both liquids and solids.
-
Separation: Once inside the septic tank, the process of separation begins. The tank is designed to be watertight and typically has two chambers. As the wastewater enters the tank, it starts to separate into three layers:
-
Top layer (scum layer): This layer consists of lighter substances like grease, oils, and floating solids. These materials float to the top of the tank.
-
Middle layer (effluent): In the middle layer, the relatively clear liquid, known as effluent, settles. This liquid contains suspended solids and bacteria.
-
Bottom layer (sludge layer): The heaviest solids settle at the bottom of the tank, forming a layer called sludge. This layer mainly consists of organic matter and solid waste.
-
-

A septic tank being lifted into place during and installation. Biological breakdown: The septic tank relies on naturally occurring bacteria to break down and decompose the organic materials in the sludge and scum layers. These bacteria work to digest and reduce the solids, transforming them into simpler substances.
-
Effluent discharge: The treated effluent in the middle layer, which is now cleaner and less harmful to the environment, exits the septic tank and flows into a drain field or leach field. In the drain field, the effluent is further purified as it percolates through the soil, where additional natural processes help filter out remaining impurities.
-
Maintenance: To keep the septic tank functioning properly, regular maintenance is essential. This includes having the tank pumped periodically to remove accumulated sludge and scum and ensuring that the system is not overloaded with excessive water use or non-biodegradable materials.
In summary, a septic tank operates by separating and treating wastewater through the natural processes of sedimentation, bacterial decomposition, and filtration. Proper maintenance and responsible water use are key to ensuring the long-term effectiveness of a septic system and protecting the environment.

